Traits that are determined by alleles carried on the X chromosome are referred to as X-linked. X-linked alleles require a specific notation: Xc or X+ where the “+†represents the dominant allele and the lowercase letter the recessive allele. Females will have two X-linked alleles (because females are XX), whereas males will only have one X-linked allele (because males are XY). Most X-linked traits in humans are recessive.
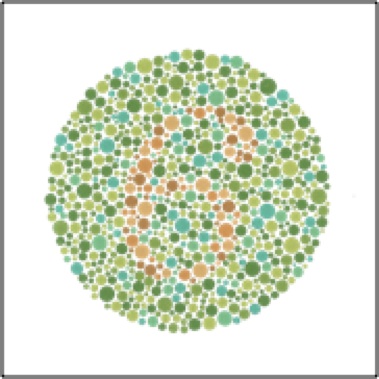
One example of an X-linked trait is red-green colorblindness. Let (Xc) represent the recessive allele that causes colorblindness and (X+) represent the normal dominant allele. Females that are X+X+ or X+Xc have normal color vision, while XcXc females are colorblind. Males that are X+Y have normal color vision, while XcY males are colorblind.
Punnett Squares
To determine the inheritance of red-green colorblindness (or any other X-linked trait), the genotypes of the parents must be considered.For example, if a mother is a carrier for colorblindness (X+Xc), and a father has normal vision X+Y, then their sons have a 50% chance of colorblindness because they inherit their X chromosome from their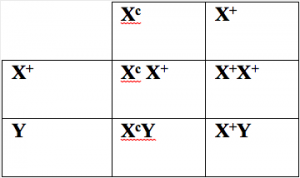 mother and their Y chromosome from their father. Their daughters will have a 50% chance of being a carrier (X+Xc) and a 50% chance of being completely normal (X+X+) (see figure). A Punnett square can be used to determine any possible genotypic combinations in the parents.
mother and their Y chromosome from their father. Their daughters will have a 50% chance of being a carrier (X+Xc) and a 50% chance of being completely normal (X+X+) (see figure). A Punnett square can be used to determine any possible genotypic combinations in the parents.
Pedigree
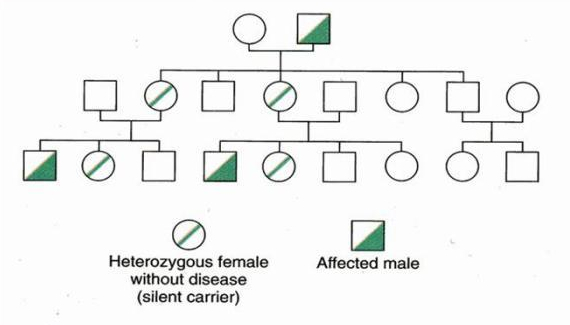
Here is a pedigree depicting X-linked recessive inheritance. These traits are often passed from a carrier mother to an affected son. X-linked traits are never passed from father to son. Males are more likely to be affected than females. In this pedigree, the carrier (heterozygous) females are indicated; however, they do not express the trait being tracked in this pedigree.
CLICK HEREÂ for an introduction to patterns of inheritance
CLICK HEREÂ to learn more about dominant inheritance
CLICK HEREÂ to learn more about recessive inheritance
